NEWS
The Integral Function of a Malting System in Craft Beer Production
Release time:
Feb 07,2026
The Integral Function of a Malting System in Craft Beer Production Craft beer has taken the world by storm, enthralling beer enthusiasts with its diverse flavors, unique aromas, and creative brewing methods. At the heart of this artisanal movement lies the malting system—a crucial component that shapes the quality and character of craft beer. Understanding the role of a malting system not only enr
The Integral Function of a Malting System in Craft Beer Production
Craft beer has taken the world by storm, enthralling beer enthusiasts with its diverse flavors, unique aromas, and creative brewing methods. At the heart of this artisanal movement lies the malting system—a crucial component that shapes the quality and character of craft beer. Understanding the role of a malting system not only enriches our appreciation of craft beer but also unveils the intricacies of the brewing process itself. In this article, we delve into the vital contributions of malting systems in craft beer production, exploring their significance, functionality, and the benefits they offer to brewers.
Table of Contents
- What is Malting?
- The Importance of Malting in Brewing
- Overview of the Malting Process
- Types of Malting Systems
- Impact of Malting on Beer Quality
- Technological Advancements in Malting
- Choosing the Right Malting System for Craft Breweries
- The Future of Malting in Craft Brewing
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Malting?
Malting is the process of converting cereal grains, primarily barley, into malt. This transformation occurs through three primary steps: steeping, germination, and kilning. During malting, enzymes are activated that convert starches in the grain into fermentable sugars, essential for brewing beer. The malting process not only prepares grains for fermentation but also significantly influences the flavor, aroma, and color of the final product. Craft brewers depend on the malting system to produce high-quality malt, which is a critical ingredient in the brewing process.
The Importance of Malting in Brewing
The importance of malting in brewing cannot be overstated. The malted grain serves as the primary source of fermentable sugars that yeast will convert into alcohol during fermentation. Additionally, malting plays a vital role in developing the beer's flavor profile, contributing sweetness, bitterness, and body. The choice of malt not only affects the beer's taste but also its mouthfeel, color, and aroma. Thus, understanding the role of the malting system is essential for craft brewers aiming to create distinctive and high-quality beers that stand out in a competitive marketplace.
Overview of the Malting Process
The malting process is intricate and consists of three main stages: steeping, germination, and kilning. Each stage is crucial for developing the unique characteristics of the malted grain.
Steeping
Steeping is the initial phase where grains are soaked in water to increase their moisture content. This process typically lasts between 24 to 48 hours, allowing the grains to absorb water, swell, and begin the germination process. Proper steeping is critical, as it prepares the grains for efficient germination and enzyme activation. The quality of water used for steeping is also vital, as it can influence the final flavor profile of the malt.
Germination
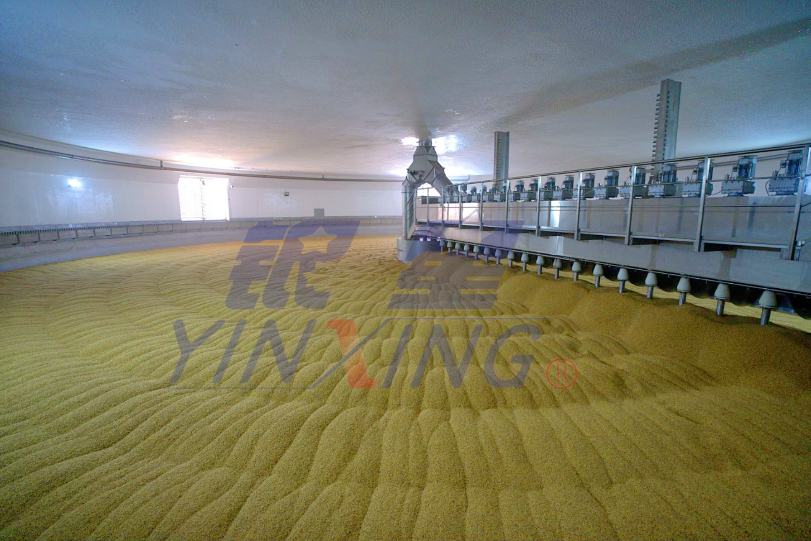
During germination, the soaked grains are spread out in a controlled environment where temperature and humidity are monitored. This stage lasts for 4 to 6 days, during which enzymes are activated that convert starches into sugars, and the grain begins to sprout. The key enzymes include amylase, which breaks down starches, and protease, which breaks down proteins. The germination process is crucial for developing the desired enzymatic activity and flavor compounds that will ultimately define the beer's profile.
Kilning
After germination, the grains are dried in a kiln to halt the growth process and preserve the enzymes. Kilning not only reduces moisture content but also develops the malt's flavor and color through the Maillard reaction. The temperature and duration of kilning can significantly impact the malt's roasted flavor, sweetness, and color, leading to various malt types, such as pale, caramel, or roasted malts. This process is essential for producing specialty malts that contribute unique characteristics to craft beers.
Types of Malting Systems
There are various malting systems available, each tailored to meet the specific needs of craft breweries. Understanding the different types of malting systems can help brewers select the correct setup for their operations.
Traditional Malting Systems
Traditional malting systems involve manual processes and are often found in smaller craft breweries. These systems typically use floor malting, where grains are spread out on a floor and turned by hand. While labor-intensive, traditional malting allows for greater control over the germination process and can yield unique flavors. However, due to the high labor costs and time required, these systems may not be practical for larger operations.
Modern Malting Systems
Modern malting systems employ advanced technology to automate the malting process, resulting in increased efficiency and consistency. These systems often utilize controlled environments and sophisticated machinery to manage temperature, humidity, and airflow, allowing for precise control over each stage of malting. While initial investment costs may be higher, modern malting systems can produce larger quantities of malt with consistent quality, making them suitable for larger craft breweries and commercial operations.
Impact of Malting on Beer Quality
The impact of the malting process on beer quality is profound. The choice of malt type, along with the specific parameters of the malting process, can greatly influence the flavor, aroma, and mouthfeel of the final product. For example, lighter malts yield beers with a crisp and clean taste, while darker malts contribute rich, complex flavors, including chocolate, coffee, and caramel notes.
Furthermore, the enzymatic activity developed during malting affects fermentation efficiency. High-quality malt facilitates optimal sugar conversion, leading to complete fermentation and a balanced flavor profile. This relationship between malting quality and brewing success is why craft brewers prioritize their malting systems and the quality of the malt produced.
Technological Advancements in Malting
As the craft beer industry continues to grow, technological advancements in malting systems are shaping the future of malt production. Innovations such as IoT-enabled sensors, automated controls, and advanced airflow systems contribute to improved efficiency, consistency, and quality of malt. These technologies allow brewers to monitor and adjust malting parameters in real-time, ensuring optimal conditions for each batch.
Moreover, advancements in genetic research are leading to the development of new barley strains that are more resistant to diseases and adverse weather conditions. These strains can produce higher yields and improved flavor profiles, further elevating the quality of craft beer. Embracing these technologies enables brewers to remain competitive while maintaining their commitment to quality and artisanal practices.
Choosing the Right Malting System for Craft Breweries
Choosing the right malting system is crucial for any craft brewery aiming to produce high-quality beer. Several factors should be considered, including the brewery's size, production goals, and desired malt characteristics. Brewers should assess their operational needs, budget, and space constraints when selecting a malting system.
For smaller craft breweries, a traditional malting system may offer the flexibility and control needed to produce unique malts, while larger operations may benefit from the efficiency and consistency of modern automated systems. Additionally, understanding the specific flavor profiles desired in the final product can guide brewers in selecting the right malting technique and equipment.
The Future of Malting in Craft Brewing
The future of malting in craft brewing looks promising as the industry continues to evolve. As consumer preferences shift towards unique and high-quality beers, the demand for specialty malts is expected to rise. Brewers are likely to experiment with innovative malting techniques, incorporating locally sourced grains and sustainable practices.
Furthermore, as technology advances, the integration of data analytics and artificial intelligence will allow for even greater precision in malting processes. This evolution will enable craft brewers to produce exceptional malts consistently, ultimately enhancing the quality of craft beer. The craft beer community's commitment to creativity and quality ensures that malting will remain a fundamental aspect of the brewing process for years to come.
Conclusion
The malting system plays an integral role in craft beer production, directly influencing the flavor, aroma, and quality of the final product. Understanding the malting process, the significance of choosing the right system, and the impact of technological advancements are crucial for both aspiring and established craft brewers. By investing in high-quality malting systems and maintaining a focus on quality ingredients, craft breweries can continue to produce exceptional beers that captivate consumers and stand out in a competitive market. The journey from grain to glass is a delicate dance, and at its core lies the malting process—an art form that shapes every sip of craft beer.
FAQs
1. What grains are commonly used for malting in craft beer production?
The most common grain used for malting in craft beer production is barley. However, other grains like wheat, rye, and oats can also be malted for specific styles of beer.
2. How does the malting process affect the flavor of craft beer?
The malting process influences the flavor of craft beer by developing fermentable sugars and unique flavor compounds during steeping, germination, and kilning. Different malt types contribute distinct flavors, aromas, and colors.
3. Can small craft breweries benefit from malting their own grains?
Yes, small craft breweries can benefit from malting their own grains, as it allows them to create unique malt profiles and maintain greater control over their ingredients. However, the process can be labor-intensive and requires careful management.
4. What are specialty malts, and how do they enhance craft beer?
Specialty malts are malted grains that have undergone specific kilning processes to develop unique colors and flavors. They enhance craft beer by adding complexity, sweetness, and distinctive characteristics that differentiate various beer styles.
5. How can brewers ensure the quality of their malt?
Brewers can ensure the quality of their malt by selecting high-quality grains, monitoring the malting process closely, and utilizing appropriate technology. Conducting regular quality checks and collaborating with reputable malt suppliers also contribute to consistency and quality.
keywords
Previous Page: